What is Hangxiety? The Science Behind it and How CBD Can Help
Hangxiety – in case the headache wasn’t bad enough…
Hangxiety is a term that describes the heightened anxiety that you feel after a night of drinking.
It is caused by your body’s attempt to rebalance the chemical changes that alcohol created the night before.
Neurotransmitters GABA (relaxation), glutamate (excitement) and noradrenaline (fight or flight) are the primary victims of alcohol’s yo-yo effect, causing you to experience extreme highs and lows.
But, good news! CBD helps to regulate those same neuro-chemical messengers, but without the risk of falling into the same rollercoaster cycle of ‘flood and deplete’.

David Nutt, professor of neuropsychopharmacology at Imperial College, London, is the scientist who was fired in 2009 as the government’s chief drug adviser for saying alcohol is more dangerous than ecstasy and LSD.
When Nutt explains the mechanics of how alcohol causes crippling anxiety, he points to some pretty specific neuro-chemical reactions. Let’s start by getting a better understanding of the chemicals at play and their roles in your brain and body.
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)

Alcohol targets the GABA receptor, which sends chemical messages through the brain and central nervous system to inhibit the activity of nerve cells.
Put simply, it calms the brain, reducing excitement by making fewer neurons fire. “Alcohol stimulates Gaba, which is why you get relaxed and cheerful when you drink,” explains Nutt.
After the first couple of drinks, that GABA is flowing and you’re starting to feel relaxed.
Glutamate
The next couple of drinks is when you really start to let loose, and that is due to the next phase of neurotransmitter activity: the inhibition of Glutatamate.
After 3 or 4 drinks your brain starts to block glutamate, which is the main excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain. The relationship between glutamate and GABA is like a see-saw, as demonstrated in the image below.
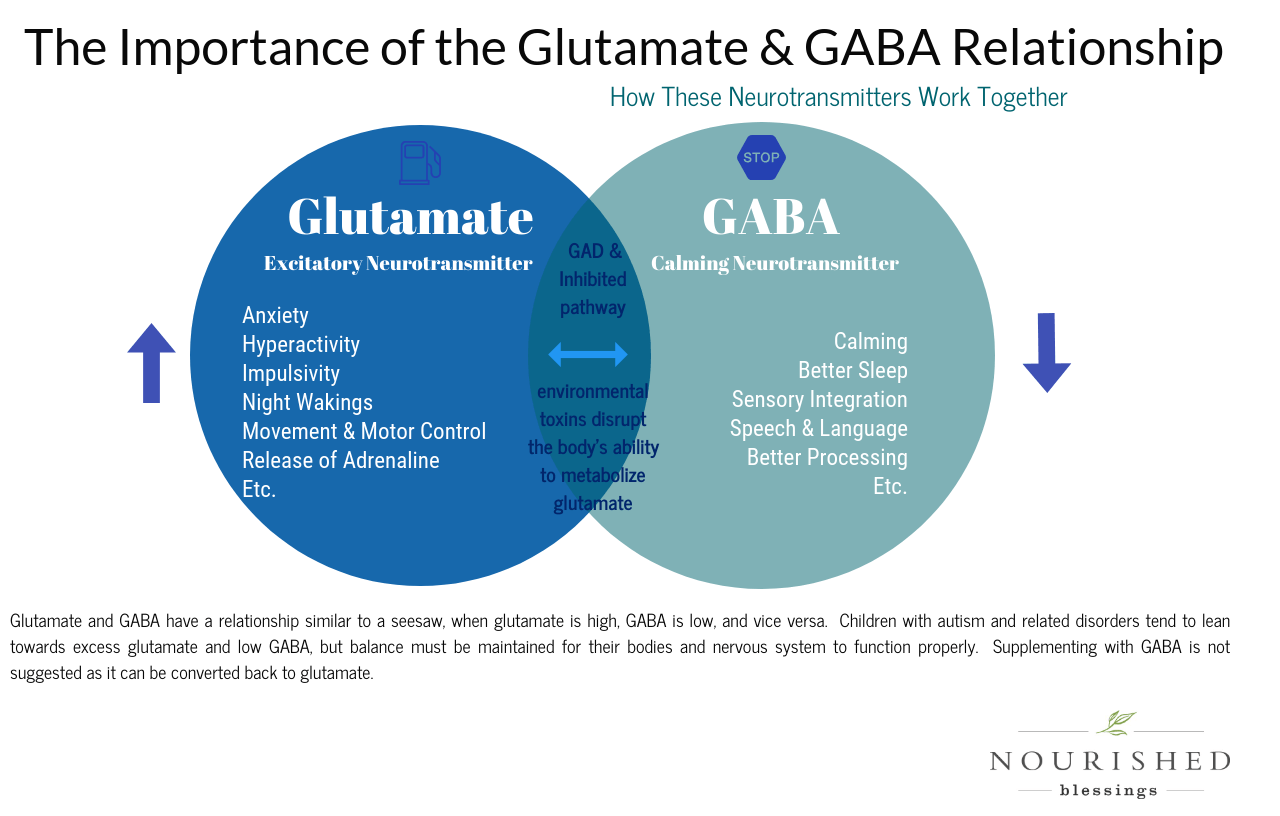
“More glutamate means more anxiety,” says Nutt. “Less glutamate means less anxiety.” This is why, he says, “when people get very drunk, they’re even less anxious than when they’re a bit drunk” – not only does alcohol reduce the chatter in your brain by stimulating GABA, but it further reduces your anxiety by blocking glutamate. (The Guardian)
Noradrenaline
Alcohol also causes a small rise in noradrenaline, a chemical messenger known as ‘the fight-or-flight hormone’.
“Noradrenaline suppresses stress when you first take it, and increases [stress] in withdrawal,” says Nutt. “Severe anxiety can be considered a surge of noradrenaline in the brain.”
Again, there is a chemical reaction happening while the alcohol is kicking in and first streaming through your bloodstream that is causing you feel like you don’t have a care in the world. But, in reality (read: scientifically) alcohol is bringing you up just to create a further fall once the drinks stop flowing.
Withdrawal: Your Body’s Attempt to Rebalance
Your body registers this new brain-chemical imbalance – higher GABA, less glutamate, changing noradrenaline levels – and attempts to make things right.
Think about what happens when you go too hard on the sweets:
Your body goes into insulin-producing overdrive to get your blood sugar levels down to normal. Then, as soon as the sweets have been digested, all that insulin causes your blood sugar to crash.
When you are drunk, your body goes on a mission to bring GABA levels down to normal and turn glutamate back up to correct the imbalance.
So, when you stop drinking, you end up with unnaturally low GABA function and a spike in glutamate – a situation that leads to anxiety. This change in brain chemistry can lead to seizures as well, which is why people have fits in withdrawal.
CBD and the Good Kind of Retrograde
Let’s hit the obvious points first:
- Cannabidiol (CBD) can help regulate GABA levels to increase relaxation
- CBD blocks glutamate in order to reduce anxiety
- CBD affects your stress response by regulating synaptic activity of noradrenaline and serotonin.
This is all great, but didn’t we just say this is exactly what alcohol does? So, what is the difference between CBD and alcohol creating these chemical reactions?
It’s all about Retrograde Signaling and plasticity: the true power of the Endocannabinoid System.
Retrograde Signaling
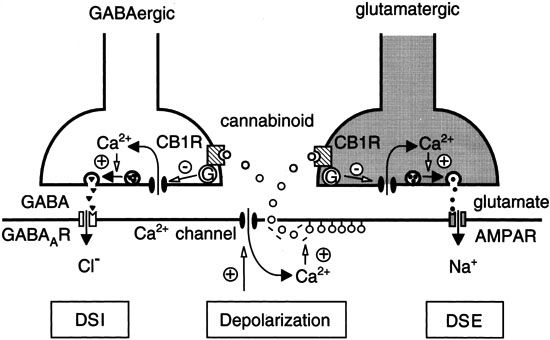
Endocannabinoids are ligands (molecules) that act as signaling messengers.
The special thing about endocannabinoids? They do not follow the typical path for chemical synaptic signaling.
Usually, a neurotransmitter flows from a presynaptic neuron to a postsynaptic neuron and attaches to a specific receptor.
- Think back to science class when you learned about neurotransmitters – the analogy of a lock and key was always used to describe how the chemical messenger fits into the appropriate receptor site. That sums up the traditional path.
Instead, what is seen with endocannabinoids is retrograde inhibition. (Lab Roots)
- The ligands (endocannabinoid molecules) will travel backward from the postsynaptic neuron to the presynaptic neuron.
Endocannabinoids actually change neurotransmitter activity between synapses by regulating the signals being released from the presynaptic site.
They aren’t just controlling how messages are being received, they are controlling how they are being sent.
Retrograde signaling increases action potential (activity) from the presynaptic site, which results in an increased number of receptors at the postsynaptic site.
- In other words, by changing the receptivity of the postsynaptic recepotors, retrograde signaling promotes binding with neurotransmitters being released at the presynaptic site.
Another increase of neurotransmission will be triggered until:
- Communication is strong AF and no further intervention is necessary
- Higher resolution synapses are formed
- Plasticity is achieved.
Creaing Lasting Change through Plasticity
Plasticity describes the brain’s to adapt to new information in order to actually create lasting change.
This is why there is no known risk for dependence when it comes to CBD use; no withdrawls.
It’s like the old saying: “give a man a fish, and you feed him for a day. Teach a man to fish, and you feed him for a lifetime.”
- Alcohol “feeds” you temporarily, while Endocannabinoids are teaching your brain how “to fish”.
The role of endocannabinoids as a way for neurons to regulate the strength of their synaptic inputs is actually perfectly demonstrated by their ability to to regulate “excitement” (or anxiety) via GABA and Glutamate activity!
This is a lot of science, I know, but bear with me. We are almost done!
This is also the difference between CBD and painkillers when it comes to the pain and inflammation response.
- CBD doesn’t just block pain receptors like some pharmaceuticals do.
- Your ECS, with help from CBD, can regulate your immune response and the resulting neurotransmitter activity.
- CBD works through various pathways of the body. It binds to cells of the immune system and directs action of these cells via the retrograde signaling system.
The TONIC Difference

TONIC goes further to help CBD do its job and create consistent, efficient results. We do this through the use of synergistic plant-based ingredients like black seed oil, ashwagandha, lemon balm and passionflower.
Black Seed Oil
Black seed oil works to reduce inflammation through its high concentration of beneficial phytochemicals like thymoquinone.
Our cold-pressed, organic black cumin seed oil has a powerful antioxidant, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory benefits, making it a great complement to CBD.
Ashwgandha
Ashwagandha is a powerful adaptogen. Like CBD, ashwagandha adapts to what your body needs in order to maintain optimal internal balance despite a changing external environment.

Ashwagandha has been clinically proven to lower cortisol levels. Cortisol is the stress hormone that contributes to our fight-or-flight response. Very similar to the noradrenaline we discussed before, remember?
So, while CBD is taking care of things from the noradrenaline side, ashwagandha is covering cortisol. Their combined effect helps strengthen the signal to up the GABA and lower the glutamate! By working together, the two cover more ground and increase your chances at keeping stress and anxiety at bay.
Lemon Balm and Passionflower
Lemon balm and passionflower both work to regulate GABA levels.
They work similarly to benzodiazepines (sleeping pills), but in a way that is sustainable for the body therefore avoiding the hangover effect that pills like that can often cause.

Again, they work together with CBD to create more reliable effects.
The Entourage Effect Goes Beyond Cannabinoids
The thing to remember about CBD and cannabis in general:
- It is very dependent on our individual body chemistry and unique Endocannabinoid System.
This means that it could require different dosages or different CBD:THC ratios, etc, for 2 people to achieve the same effect.
We guard against this by reinforcing CBD with other plants that elicit similar effects and help CBD along its journey, creating a more predictable and individualized wellness solution.


 The Steady Supply
The Steady Supply

 Personalized Vibes
Personalized Vibes
